The healthcare industry across hospitals, doctor’s offices, clinics and nursing facilities in the U.S. made a shift from paper-based systems to digital recordkeeping in recent years. The shift from paper to digital records required significant financial commitment from the federal government and health organizations who spent billions on the necessary hardware, software and training. The healthcare sector’s rapid transformation makes digitizing patient information fundamental to improving medical service quality and efficiency.
Electronic Medical Records (EMR) lead the digital transformation in healthcare by transforming how providers handle patient information through management, access, and exchange functionalities. This article examines the EMR system by detailing its basic features and exploring its various applications in healthcare. Healthcare professionals frequently use these terms interchangeably, leading to confusion among users. Despite their similarities, EHR and EMR possess many unique characteristics that differentiate them from each other.
What is EMR
The EMR full form is Electronic Medical Record which serve as digital equivalents to traditional paper charts and include extensive data about patient medical history along with their diagnoses, medications, treatment plans, immunization dates, allergies, radiology images and laboratory test results. Medical EMR software provides users with immediate access to centralized patient data which differs from traditional paper record systems.
What is EHR
The EHR medical abbreviation stands for Electronic Health Record (EHR), which serves as the digital record of a patient’s medical history, which healthcare providers maintain throughout time and contains essential administrative clinical information like demographics and medications, which helps improve clinical workflow. Through multiple interfaces, the EHR system helps manage care-related tasks both directly and indirectly by providing support for evidence-based decisions, quality management processes, and outcomes reporting.
Here are the core components of an Electronic Health Record (EHR):
- Patient Demographics: EHR patient demographics include basic information such as name, date of birth, address, and contact details.
- Medical History: The patient’s medical history includes detailed documentation of past illnesses along with surgeries and allergies and tracks immunizations and medications from multiple healthcare providers.
- Symptoms and Diagnoses: The record should include presenting symptoms as well as diagnoses made by various physicians during the patient’s care journey with documented treatment plans from different healthcare settings.
- Lab Results: The lab results section contains digital versions of laboratory tests together with X-ray images, imaging scans, and additional diagnostic reports sourced from multiple facilities.
- Progress Notes: Physicians and healthcare professionals keep detailed records of their observations and notes during patient consultations.
- Insurance Information: Healthcare providers can authenticate patient eligibility and advance the care process using detailed insurance coverage information.
(EMR) Electronic Medical Record Example
Amelia makes an appointment to see her family doctor for her regular health evaluation. The receptionist enters Amelia’s details into the EMR system, which establishes a digital record for her. The doctor evaluates Amelia’s medical history through her EMR, which contains details about her past diagnoses, medication records, and allergy information. After the consultation, the doctor records all new details about Amelia’s current health status, which includes symptoms, vital signs, and prescribed medications.
The lab technician gets the electronic request through the EMR system directly. Amelia’s EMR system receives automatic updates with lab test results as soon as they become available, enabling doctors to access the latest diagnostic information in real-time. The updated information allows the doctor to make informed care decisions for Amelia. Suppose Amelia is referred to a specialist. The specialist receives referral information and medical records through EMR software without any disruption.
The specialist receives a complete overview of the medical background, which optimizes the consultation efficiency and eliminates unnecessary testing. The EMR system provides centralized management of health data. It enables doctors to access relevant information in real-time while promoting efficient communication among healthcare professionals and improving patient care coordination.
EHR vs EMR: Spotting the Difference
|
EMR (Electronic Medical Records) |
EHR (Electronic Health Records) |
|
A healthcare organization uses a digital patient chart system to manage records within environments such as hospitals or clinics. |
Multiple healthcare providers and organizations receive patient information through this system, which maintains care continuity. |
|
Medical history, diagnoses, and treatments |
Data sharing across hospitals, specialists, and pharmacies |
|
Lab results and prescriptions |
Patient access through portals |
|
Doctor’s notes from past visits |
Real-time updates for coordinated care |
|
Limited (stays within one office/hospital) |
Shared across different healthcare settings |
|
A single practice records all patient medical history, including symptoms, diagnoses, treatments, medications, lab results |
The system delivers comprehensive care perspectives by integrating data from several providers and including preventive measures and immunization details. |
|
Used for decision-making |
Used for diagnosis and treatment plan |
Is Epic an EMR or HER
Epic serves as patient portal software, which provides numerous tools specifically designed for healthcare professionals and specialists. This system functions as an EHR platform (electronic health record) rather than an EMR system (electronic medical record), so it emphasizes data sharing between hospitals and clinics for regular operations and procedures. Providers generate EMRs as patient records for specific clinical visits in healthcare facilities which provide data for EHR systems. EHR systems represent extended digital compilations of patient or population health information over time.
The electronic health record represents a structured digital repository for patients’ health information and population health data. Different healthcare settings can access these medical records. Enterprise-wide information systems connected to networks or other information networks and exchanges enable the distribution of records. EHRs contain various data types such as patient demographics and medical history and extend to medication records and allergy information alongside immunization status as well as laboratory test outcomes, radiology images vital signs, personal statistics including age weight, and billing information
Clinician offices use EMRs as electronic replacements for traditional paper charts, which serve as an internal system within their practice. The EMR system maintains records of medical and treatment histories for patients who receive care at that particular practice.
Epic’s Capabilities as an EHR
The system enables different healthcare systems to share patient records with each other.
- Supports patient portals for engagement.
- Integrates with billing, scheduling, and analytics.
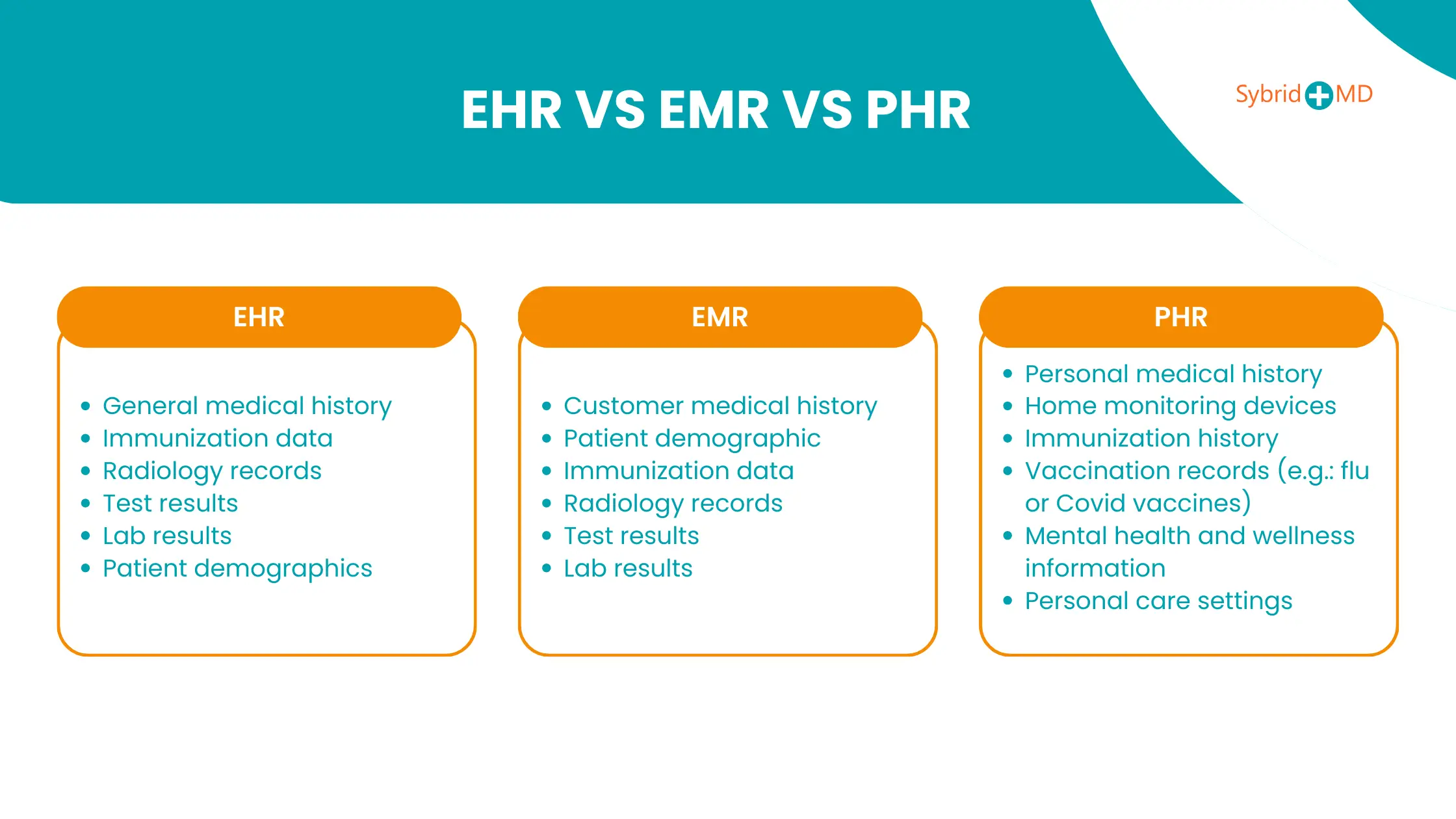
EHR vs EMR vs PHR
EHR
EHR full form is Electronic Health Records (EHR) which provide a unified medical history that healthcare organizations can share across their networks. EHRs serve as critical tools for healthcare collaboration which allows providers to make informed treatment decisions by accessing complete patient medical records. The system enhances the coordination of patient care and boosts efficiency while enabling precise medical decision-making through comprehensive health data access.
- General medical history
- Immunization data
- Radiology records
- Test results
- Lab results
- Patient demographics
Read the Issues and Solutions of EHR here!
EMR
An Electronic Medical Record (EMR) represents a longitudinal electronic documentation of health data for a patient that comes from multiple healthcare encounters within a treatment setting. This information encompasses patient demographics together with progress notes and problems as well as medications, vital signs, past medical history, immunizations, laboratory data, and radiology reports. The EMR functions to automate clinical processes and enhance workflow efficiency for clinicians.
- Customer medical history
- Patient demographic
- Immunization data
- Radiology records
- Test results
- Lab results
Read the EMR benefits here!
PHR
PHRs serve as digital health records that contain medical data that patients themselves manage. Online access to PHRs enables patients to view their medical test results along with prescription details and allergy information. Individuals can manage their medical records through the addition of medical history information and personal data while tracking their health status. Older patients become more actively involved in their healthcare through the use of PHRs, which serve as a critical component in care transition interventions.
- Personal medical history
- Home monitoring devices
- Immunization history
- Vaccination records (e.g.: flu or Covid vaccines)
- Mental health and wellness information
- Personal care settings
What Are the Benefits of EHR, EMR, and PHR Integration?
Enhanced Patient Outcomes:
Integrated healthcare systems enable providers to access complete patient medical records instantly including EHR details alongside family medical histories and home monitoring device data. Complete access to medical information enables healthcare professionals to make more precise diagnoses and develop better treatment strategies.
Improved Communication:
The combination of health record systems with messaging platforms and online portals creates better communication channels between medical professionals and patients. Through integrated systems, patients can access provider contact information and receive prompt updates about their health status and laboratory test results.
Operational Efficiency
The integration of EMR and EHR systems with billing or scheduling software enables healthcare facilities to function more effectively by reducing administrative tasks and allowing health professionals to dedicate more time to patient care.
Sustainability
Healthcare facilities produce multiple petabytes of data every year. Implementing digital medical records represents an environmental advancement as they dramatically reduce paper use by nearly 50%.
Accessibility
Medical care quality is being enhanced by easy access to patient records. Doctors have immediate access to data for improved treatment decisions without waiting days for archival records. And referrals are faster. Emergency appointments proceed without delays from paperwork processing.
Healthcare informatics and healthcare analytics professionals require a thorough understanding of EHRs and EMRs to perform their roles effectively. People often use EHR and EMR interchangeably, but these terms actually refer to different things. An EMR contains a patient’s medical history as recorded by one particular healthcare provider’s practice. The EMR represents a detailed record that relates to a single healthcare practice. An EHR functions as a unified collection of EMRs from multiple healthcare providers, which together create a complete overview of patient data.
FAQs:
What is the difference between EMR and EHR?
The primary distinction between an EMR system and an EHR system is that EMR systems store healthcare information for patients and procedures within specific hospitals or healthcare businesses. EHR systems enable the exchange of this data between different institutions.
Is Epic considered an EMR or EHR?
Epic offers patient portal software that includes multiple tools designed specifically for healthcare professionals and specialists. This system operates as an EHR system that focuses on electronic health records instead of an EMR system dedicated to electronic medical records because it enables interoperable data exchanges between hospitals and clinics for routine procedures and operations.
What is the difference between EMR and ERP?
EMR systems are designed for internal use within one healthcare facility, whereas ERP systems operate across multiple business functions beyond healthcare
Can EMR and EHR be used interchangeably?
EMR and EHR systems serve different purposes and cannot be substituted for one another. EMRs only store patient data within one healthcare organization, while EHRs enable healthcare providers to share patient information across different facilities for coordinated care.
What are the top 3 EHR systems?
The three top EHR systems most commonly used in the healthcare industry are:
- Epic Systems: Epic Systems excels with comprehensive interoperability features alongside a user-friendly interface and the powerful MyChart patient portal. Used by major hospitals and healthcare networks.
- Cerner (now Oracle Health): The system delivers powerful data analytical tools alongside population health management features and integrates smoothly across various healthcare settings.
- MEDITECH: MEDITECH stands out as the preferred EHR system among small and mid-sized hospitals because it delivers efficient and affordable solutions which enhance clinical workflows.
Is Cerner an EHR?
Oracle now owns Cerner which provides various healthcare solutions for medical businesses, patients, insurance companies and government agencies. Their product range contains an electronic health record system (EHR system). Cerner functions as an EHR system but does not operate as an EMR system.