The United States faces a substantial challenge from obesity as it damages individual health outcomes while placing demands on the entire healthcare system. Immediate attention and suitable actions are necessary to address the risks linked to obesity. Healthcare providers file reports for weight loss counseling services with specific ICD 10 weight loss counseling codes. It outlines the ICD-10 codes that healthcare professionals generally apply when reporting weight loss counseling services.
ICD 10 Abnormal Weight Loss
Abnormal weight loss signifies possible health problems that include metabolic disorders and persistent conditions like cancer and gastrointestinal diseases or malnutrition. Healthcare providers must analyze the reason for weight loss and make records of any associated health issues. The ICD-10 code R63.4 documents instances of weight loss that deviate from normal patterns with no identifiable cause. This disease produces a substantial decline in body weight without any dieting or physical exercise. A 5% body weight reduction that occurs over a 6 to 12-month period without any specific reason qualifies as abnormal weight loss.
Anorexia With Abnormal Weight Loss ICD 10
Eating disorders include multiple different medical conditions. These disorders are associated with how people perceive food and their body image while existing in three primary forms. Excessive dieting and exercise that lead to dramatic weight loss characterize the eating disorder known as anorexia nervosa. Another common condition is bulimia nervosa. Individuals with this disorder consume excessive amounts of food and then use purging methods or other weight loss actions to make up for their binging episodes. Binge eating is a related eating disorder. Individuals who suffer from this disorder consume large amounts of food in binges without engaging in purging behaviors.
The ICD-10 Code for Anorexia Nervosa
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes provide a standardized language for the industry to classify various medical conditions. ICD codes provide a clear communication tool for hospitals, insurance companies, healthcare providers, and other professionals in the medical field. Organizations covered by HIPAA adopted the ICD-10 system starting in 2015. The appropriate ICD-10 coding enables treatment professionals and insurance companies to develop an accurate understanding of the medical disorder.
A provider needs to conduct a full medical history review and a complete evaluation of the client’s symptoms to determine the correct code. Parents often become worried and take their children to visit a healthcare provider when they notice signs of distress. Clients sometimes go to their doctors or clinics without parental involvement. Anorexia nervosa affects females more than males, and younger women experience it more frequently than older women. Multiple diagnostic codes exist to classify anorexia nervosa. They are as follows:
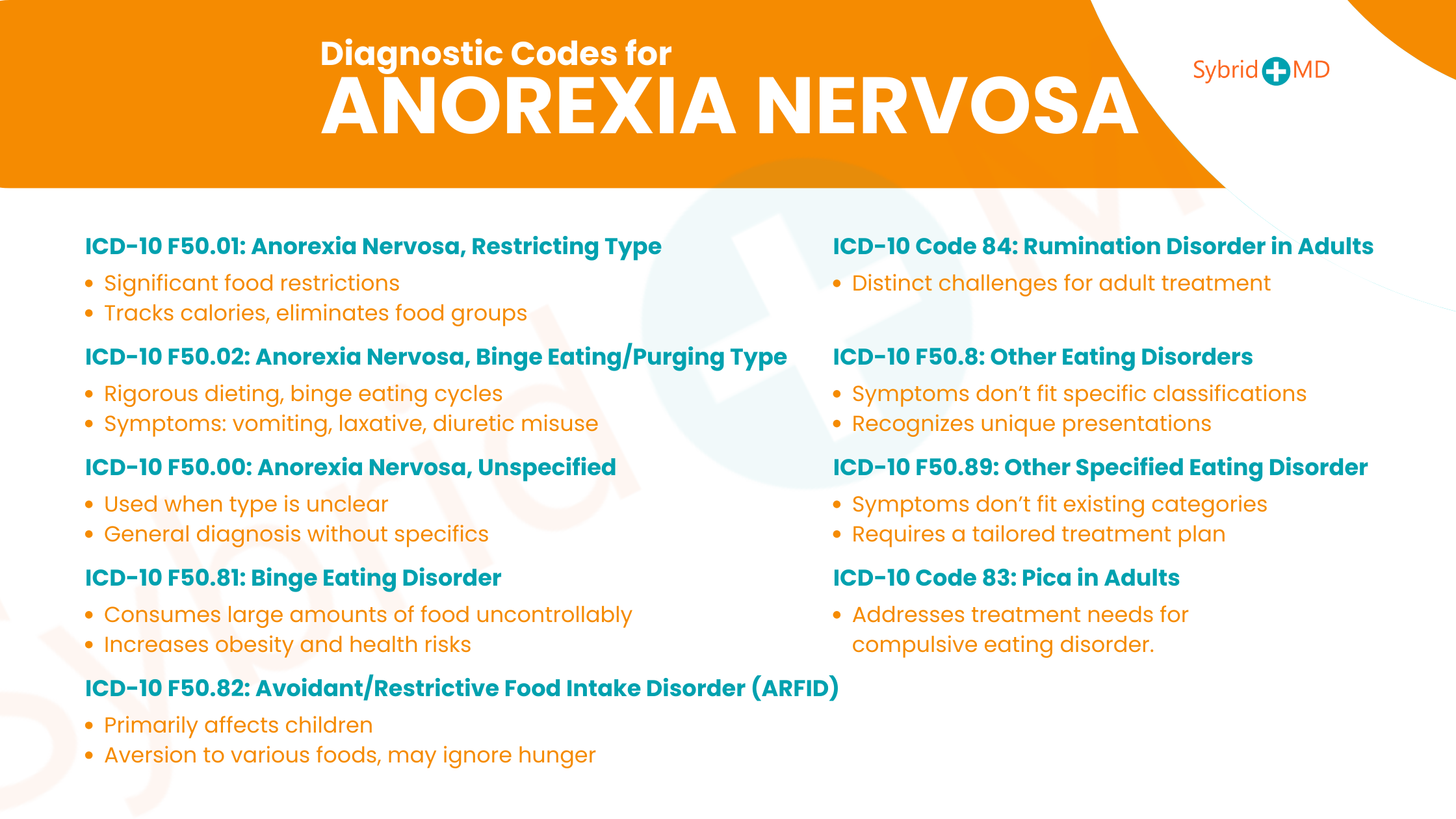
1. ICD-10 F50.01: Anorexia Nervosa, Restricting Type
The ICD-10 classification F50.01 describes anorexia nervosa of the restricting type, which features substantial food consumption restrictions. Patients with this disorder compulsively track their calorie intake. Individuals with this condition meet their daily calorie intake goals through the elimination of certain meals. Patients with restricting anorexia nervosa must eliminate particular food groups, such as carbohydrates, from their meals. Certain individuals exclude foods from their diets according to their colors or textures.
2. ICD-10 F50.02: Anorexia Nervosa, Binge Eating/Purging Type
Anorexia nervosa with binge eating/purging type classification has the ICD-10 code F50.02 and exhibits distinctive characteristics. Individuals with this condition must enforce rigorous dietary restrictions. The binge eating/purging type of anorexia nervosa includes alternating cycles of extreme food consumption and purging actions. The binge eating/purging subtype of anorexia nervosa displays a combined disorder that incorporates features from both anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa.
People eliminate contents from their bodies through vomiting or by using laxatives and diuretics. Laxatives help soften stool to enable bowel movements, while diuretics work by reducing fluid buildup in the body. People sometimes use enemas as a method to clear their bowels during specific situations. People suffering from anorexia nervosa and/or bulimia nervosa improperly use medical products such as laxatives and diuretics to achieve their goals despite these products having essential medical functions.
3. ICD-10 F50.00: Anorexia Nervosa, Unspecified
When a specific type of anorexia nervosa cannot be determined, the ICD-10 code F50.00 should be used. This code indicates anorexia nervosa, unspecified. Certain clients experience condition changes while they move through varied situational experiences. The precise situation remains unclear, but the diagnosis of anorexia nervosa for the client stands obvious. ICD-10 codes assigned to clients may require updates based on new data or client progress during treatment.
4. ICD-10 F50.81: Binge Eating Disorder
Binge eating disorder is characterized by consuming large quantities of food. Eating a large quantity of food during special dinners is different because it doesn’t include a loss of control. Individuals who experience binge eating episodes find themselves unable to manage both the types and quantities of their food intake. The challenge of handling regular binge eating stems from its classification as weekly episodes that persist over several months. This condition increases the risk of developing obesity and related diseases like diabetes, high cholesterol levels and high blood pressure.
5. ICD-10 F50.82: Avoidant/Restrictive Food /Intake Disorder
The disorder known as Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder carries the abbreviation ARFID. The International Classification of Diseases code F50.82 categorizes this condition. The eating condition ARFID can occur in people across all age groups, but it mainly affects children. Children who suffer from ARFID struggle with eating various types of food. In some cases, their aversion to food becomes so overpowering that they lose interest in consuming anything. The affected individuals generally refuse to acknowledge hunger while showing no enjoyment in eating.
6. ICD-10 F50.8 – Other Eating Disorders
When it becomes evident that a client suffers from an eating disorder that doesn’t match any specific classification, the ICD-10 code F50.8 is appropriate. This classification helps clinicians because some clients present symptoms that do not conform to conventional diagnostic categories. Each individual’s presentation is unique.
7. 84: Rumination Disorder in Adults
The medical coding system has created a specific code for rumination disorder in adults to recognize the condition’s distinct challenges and treatment strategies for adult patients.
8. ICD-10 F50.89: Other Specified Eating Disorder
When a situation can’t be classified under existing eating disorder categories, the code F50.89 can be used to represent other specified eating disorders. Clients can exhibit symptoms and behaviors that deviate from the typical presentations of anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa. A client might present with a mix of symptoms that do not align with established eating disorder categories. The selection of this code indicates to healthcare providers that the eating disorder does not match any classic category of eating disorders. The client needs a distinct treatment plan because their condition doesn’t match typical diagnostic categories.
9. 83: Pica in Adults
Adults with the compulsive eating disorder Pica now have an official medical code that helps to identify separate treatment needs from those used in pediatric cases.
ICD 10 Code For Abnormal Weight Loss In Newborn
Newborns suffering from abnormal weight loss present a serious health issue needing correct identification and medical intervention. The ICD-10 coding system assigns the code P92.6 to newborns with abnormal weight loss, representing a failure to thrive in newborns. The P92.6 code captures all scenarios involving abnormal weight gain ICD-10 or excessive weight reduction in newborns.
The ICD-10 system uses codes R63.4, P92.x, P92.6, R62.51, and the P07 series32 to categorize abnormal weight loss in newborns.
ICD 10 Code For Abnormal Weight Loss
- 4 Abnormal weight loss: Find this code by searching for the primary terms ‘Loss’ or ‘Weight’ followed by “Loss/weight” or “Weight/loss” in index3. The code R63.41 must be assigned when a newborn’s weight loss exceeds 10%, and treatment has been initiated. Normal weight loss for newborns ranges from 5-10%, but any loss above 10% calls for medical intervention through added feeds of expressed milk or formula.
- x: Feeding problem of newborn3.
- 6 Failure to thrive in newborns: Assign this code to newborns who have not reached their 28th day of life.
- 51 Failure to thrive (child): For children older than 28 days, use the R62.51 code. R62.51 should not be applied along with P92.6 which refers to failure to thrive in newborns.
- P07 series: Apply this code series when the infant has low birth weight and has not yet reached 28 days of age.
How will these new codes help providers and patients?
Healthcare providers and their patients will benefit from multiple advantages through the implementation of these new codes.
1. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
The former ICD-10-CM coding system demonstrated limitations when it came to effectively documenting obesity severity. The new classification system allows healthcare providers to enhance their diagnostic capabilities and management of obesity. The variability of obesity severity among pediatric patients makes precise classification essential because it changes according to age and growth patterns.
2. Enhanced Data Utility and Research
Healthcare claims data historically contained insufficient coding for obesity, which has restricted understanding of the disease’s healthcare burden and associated costs. New coding standards will enhance coding procedures which will lead to precise data collection and analysis as well as support research efforts to prevent and treat obesity. Healthcare providers and policymakers will develop stronger approaches to combat the obesity epidemic through improved data collection.
3. Reducing Stigma and Bias
Obesity patients face stigma that creates obstacles for successful treatment. The new ICD-10-CM codes minimize stigmatization by employing medical terms that concentrate on the intensity of the condition rather than using negative language. Healthcare providers should choose terms such as “Class III Obesity” instead of “morbid obesity due to exhausted calories” to establish a respectful and supportive environment within patient-provider relationships.
Conclusion
Healthcare providers need to utilize clinically relevant terms while explaining treatment options to their patients. Implementing these new codes represents a significant advancement in obesity treatment for patients across all age groups. Healthcare providers can ensure effective obesity management for their patients by adopting these codes which allow for proper diagnosis and treatment support.
FAQs:
What is considered abnormal weight loss?
The standard definition of abnormal weight loss for anorexia nervosa includes body weight below 85% of predicted norms for age, height, and sex or a BMI under 17.5 for adult patients. Patients with this condition usually restrict their caloric intake severely while engaging in excessive exercise and experience extreme fear about gaining weight. The DSM-5 identifies significant weight loss as an essential diagnostic criterion for anorexia nervosa, which results in malnutrition along with organ dysfunction and other severe complications. Anorexia nervosa receives classification under ICD-10 code F50.0, where the level of weight loss severity depends on BMI thresholds.
What is the CPT code for abnormal weight loss?
The ICD-10 code R63.4 identifies abnormal weight loss, but CPT codes do not exist for this diagnosis because they represent procedures and services instead of medical conditions.
What is the ICD-9 code for abnormal weight loss?
Abnormal weight loss is categorized under ICD-9 code 783.2.
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal diet?
The ICD-10 code Z72.4 applies to abnormal diets. The World Health Organization lists it under the category of Factors influencing health status and contact with health services for inappropriate diet and eating habits.
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal weight loss?
R63.4 represents the ICD-10 code for abnormal weight loss. The medical code represents unexplained weight loss, which deviates from normal patterns.
What is diagnosis code F41 1?
The ICD-10 diagnosis code F41.1 identifies “Generalized Anxiety Disorder” (GAD) as a mental health issue that involves persistent and excessive worry about different situations with daily functioning effects.